It is a spreadsheet program which is used to save and analyse numerical data.
In this blog, Vibgyor is trying to present you the important features of MS Excel, along with an overview of how to use the them, their benefits etc.
Following are the features which makes excel an important tool for everyone:
What is MS Excel?
MS Excel is a spreadsheet program which is used to store data in tabular form. Analyzing data using an Excel sheet is very easy for anyone.
Below is an image of basic Excel spread sheet :

How to open MS Excel?
You can open and start using MS Excel on your Laptop/Desktop as below:
Click on Start ---- All Programs -- MS Office --- MS Excel.
Alternatively, you can just type MS Excel in the search option available to the right of Windows icon in bottom left pane of your home screen.
Rows,Columns and a cell?
As we discussed above, MS Excel is a program which is used to store data in tabular form.
It is a set of facts and figures which are presented in an organised way in rows and columns
Raws run horizontally, while Columns run Vertically (Pic Below:)

A Cell :
The rectangular box formed by the intersection point between rows and columns is called a cell.

What is Cell Address?
Cell address is referred to as name of cell formed by the intersection of rows and columns. It is spoken as Column name followed by row name. Like,if row 5 is intersected in column H then the cell address is H5.

Features of MS Excel:
Now you know that numerous editing and formatting can be done on an Excel spreadsheet.
Excel has a lot of features which make it easy to present, analyse and use data as per our requirement. All these features are seen on top ribbon as we open any Excel Sheet.
Pic below shows the various features of MS Excel (shown in image):

Home
This menu has options like adjusting of font size, font styles, font colour, background colour, alignment, formatting options and styles, insertion and deletion of cells and editing options.
Insert
This menu consists of options like inserting tables, changing their format and style, inserting images and figures, adding graphs, charts etc, inserting header and footer options, symbols and equation.
Page Layout
In this option, we can set up Themes, orientation and page setup
Formulas
If you want fast solutions to a large amount of data stored in tables in MS excel, you can add formulas from this option.
Data
Adding external data (from the web), filtering options and data tools are available under this category
Review
This option has options like Spell Check, links check etc. Also if you would like to add some comment to any data which can be used later to remember, you can do the same under thus option
View
Under this option, Zoom in and Zoom out features are available. Different views in which we want the spreadsheet to be displayed can be edited here.
Benefits of Using MS Excel
MS Excel is widely used for various purposes because the data is easy to save, and information can be added and removed without any problem and less hard work.
Given below are some important benefits of using MS Excel:
Easy To Store Data: Since there is no limit to the amount of information that can be saved in a spreadsheet, MS Excel is widely used to save data or to analyse data. Filtering information in Excel is easy and convenient.
Easy To Recover Data: If the information is written on a piece of paper, finding it may take longer, however, this is not the case with excel spreadsheets. Finding and recovering data is easy.
Application of Mathematical Formulas: Doing calculations has become easier and less time-taking with the formulas option in MS excel
More Secure: These spreadsheets can be password secured in a laptop or personal computer and the probability of losing them is way lesser in comparison to data written in registers or piece of paper.
Data at One Place: Earlier, data was to be kept in different files and registers when the paperwork was done. Now, this has become convenient as more than one worksheet can be added in a single MS Excel file.
Neater and Clearer Visibility of Information: When the data is saved in the form of a table, analyzing it becomes easier. Thus, information is a spreadsheet that is more readable and understandable.
MS Excel – Points To Remember
There are certain things which one must know with respect to MS Excel, its applications and usage:
An MS Excel file is saved with an extension of .xls
Companies with large staff and workers use MS Excel as saving employee information becomes easier
Excel spreadsheets are also used in hospitals where the information of patients can be saved more easily and can be removed conveniently once their medical history is cleared
The sheet on which you work is called a Worksheet
Multiple worksheets can be added in a single Excel file
This is a data processing application
Shortcuts in MS Excel –
Excel has inbuilt shortcuts options that help you to do things even easier and faster.
Given below is an image which can be used to watch all excel shortcuts. We will also explain about all shortcuts one by one after the image.

Shortcuts
1. Double Click for a Quick AutoFill
The AutoFill technique is used to copy formulas, date sequences and Custom Lists amongst many others. It’s a brilliant tool that greatly improves data entry and the copying of formulas.
The AutoFill technique can be performed even quicker by double clicking on the AutoFill handle. This will only work for as long as the column to its left has content.

2. Duplicate Cell Content
Something Excel demands is a lot of data entry. All those rows of data have to come from somewhere and unless there is a connection to a data source then it is being entered.
The Ctrl + D shortcut stands for duplicate and repeat the content of the cell above. I heavily rely on this shortcut as often the next row uses the same date, name or category as the previous row. This saves time and improves accuracy.
The great thing about Ctrl + D is that it copies the cell’s formatting as well as its content. There is also the Ctrl + ‘ shortcut which only copies the content.
3. Navigate with the Name Box
The Name Box to the left of the Formula Bar can be used to navigate an Excel spreadsheet. It is great for leapfrogging large amounts of data. So even if you do not know the exact cell reference that you need, you can jump to the rough area of where you need to be.
Click inside the Name Box, type the cell reference you want to go to and press Enter.

To quickly switch between the sheets of a workbook use the Ctrl + Page Up and Ctrl + Page Down keyboard shortcuts. Using these shortcuts saves having to click on the little tabs at the bottom of the book each time.
5. Quickly Enter Today’s Date
Never have to check the calendar or type those pesky forward slashes again when entering today’s date, as the Ctrl + ; shortcut is there to do it for you.
6. Select the Current Region
One of the most beautiful keyboard shortcuts in Excel must be Ctrl + Shift + 8. This shortcut will select your current region. This means it selects all the cells in the range that you are currently within.
Selecting hundreds and thousands of cells just became easy.
7. Format Cells, Please
Format Cells is the most important dialog box in Excel. There you go, I said it. It’s more important than Print, Page Setup or Data Validation. And because of this, the keyboard shortcut should be known and used.
Its Ctrl + 1.
A common task in Excel is to copy formatting from one cell to another. It could be that you want to copy the specific shade of colour you used to fill another cell, a custom format or some conditional formatting rules.
The Format Painter is a fantastic tool that will enable you to do all of the above.
1. Select the cell that contains the formatting you want to use.
2. Click the Format Painter button on the Home tab.
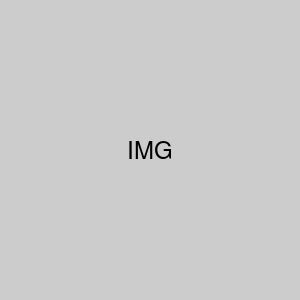
3. Select the cell(s) you want to apply the formatting to.
Double click the Format Painter button to keep it on so that you can paint the formatting to multiple ranges. Just remember to click the Format Painter button again when you are finished to turn it off.
Formatting
9. Wrap Text
Formatting
If you are using a column in your Excel spreadsheet to store a description or comments, you need to know how to wrap text. Wrap text will display content on multiple lines within a cell to make it visible no matter how much you type.
1. Select the cells that you want to apply wrap text to.
2. Click the Home tab on the Ribbon.
3. Click the Wrap Text button in the Alignment group.
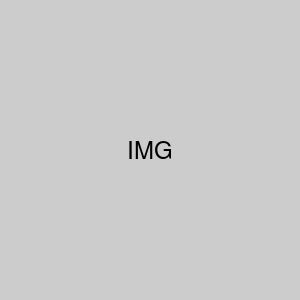
10. Clear Cells
Pressing the Delete key in Excel only removes the contents of a cell. It will not remove formatting, Data Validation, comments or hyperlinks.
If a cell is not properly cleared it can cause problems in the future by formatting cells incorrectly, or preventing data from being entered due to validation rules.
1. Click the Clear cells button in the Editing group of the Home tab.
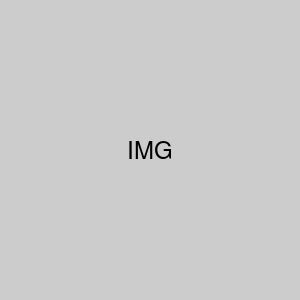
2. Select the option you want from the list.
The date can be formatted to show the day of the week in a cell. This is not one of the provided date formats by Excel, but can be created as a custom format.
1. Select the cell(s) you want to format.
2. Click the Home tab on the Ribbon.
3. Click the Number Format list arrow in the Number group and select More Number Formats.
4. Select Custom from the Category: list.
5. Enter dddd in the Type: box.
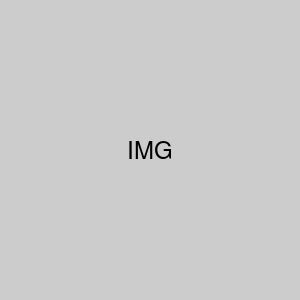
6. Click Ok.
The Conditional Formatting tool can be used to bring your attention to almost anything you care to monitor in an Excel spreadsheet.
To be notified if a date occurs this month;
1. Select the range of cells containing the dates that you want to check.
2. Click the Home tab of the Ribbon.
3. Click the Conditional Formatting button in the Styles group.
4. Select Highlight Cell Rules and then select A Date Occurring.
5. Click on the drop list arrow and select This Month.
6. Choose a format from the second drop list arrow.
7. Click Ok.
You may need to be made aware of dates that have passed on a spreadsheet such as an expiry date of a contract, or the due date of a payment.
By using the TODAY function within a Conditional Formatting rule it is possible to format the cells containing dates that have passed. This makes it easy to identify them on a spreadsheet.
1. Select the cells that contain the dates you want to format.
2. Click the Conditional Formatting button on the Home tab.
3. Select New Rule from the menu.
4. Select the Format only cells that contain rule type from the list.
5. In the rule description area change between to less than.
6. In the box to the right, enter =TODAY().
7. Click the Format button and select the formatting you wish to apply to dates in the past.
8. Click Ok.
Formulas
14. TODAY() and NOW()
The TODAY and NOW functions are used to calculate the current date. This is extremely useful as by finding the current date you can calculate how long it has been since a specific date, or how long until an important due date.
The TODAY function returns today’s date, and the NOW function returns today’s date and the current time.
These functions require no arguments and can be entered into a cell as below.
=TODAY()
=NOW()
An example of its use to calculate the number of days until a due date (cell A2) is shown below.
=A2-TODAY()
15. Use COUNTA() to Count All Non-Blank Cells
Microsoft Excel contains many statistical functions, which include a few variations of count functions. The COUNT function will only count the cells that contain numbers in them. Fortunately the other variations cater for anything else you may wish to count.
An important one to know is COUNTA. This function counts all the cells that are not blank. This means it counts cells containing numbers, text, formulas and even error messages as long as it has something in it.
It is written in the same way that the COUNT is. For example the function below counts all the non- blank cells in the range A2:A50.
=COUNTA(A2:A50)
16. Perform a Lookup with the Infamous VLOOKUP Function
The VLOOKUP function is the most used lookup and reference function in Excel. You have probably heard of it.
It looks for a value in the first column of the lookup table and returns an associated value from a different column of the table. The V in its name stands for Vertical. For example, it can look for a product code and return the products minimum storage temperature.
VLOOKUP requires 4 items of information (arguments) in order to work.
=VLOOKUP(lookup_value, table_array, col_index_num, [range_lookup])
· Lookup value – The value you are searching for.
· Table array – The range of cells that you want to search for the lookup value within. VLOOKUP always looks down the first column of this selected range.
· Col index num – The column number of the table array that stores the information you want to return about the value.
· Range lookup – The type of lookup to be performed. Enter TRUE for an approximate match, or FALSE for an exact match. The default option is TRUE. When using the approximate match the lookup table must be sorted by the first column.
Most VLOOKUP examples involved performing an exact match. In this example, the VLOOKUP function has been used to return the unit price of a product from the table.
=VLOOKUP($H$4,$A$2:$F$78,4,FALSE)
This blog is under construction...
Come back for more updates...






